Inertial stretching separation in binary droplet collisions
Abstract
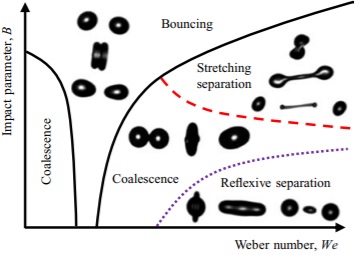
Binary droplet collisions exhibit a wide range of outcomes, including coalescence and stretching separation, with a transition between these two outcomes arising for high Weber numbers and impact parameters. Our experimental study elucidates the effect of viscosity on this transition, which we show exhibits inertial (viscosity-independent) behaviour over an order-of-magnitude-wide range of Ohnesorge numbers. That is, the transition is not always shifted towards higher impact parameters by increasing droplet viscosity, as it might be thought from the existing literature. Moreover, we provide compelling experimental evidence that stretching separation only arises if the length of the coalesced droplet exceeds a critical multiple of the original droplet diameters (3.35). Using this as a criterion, we provide a simple but robust model (without any arbitrarily-chosen free parameters) to predict the coalescence/stretching-separation transition.